 How is the PALS Tachycardia Algorithm Utilized?
How is the PALS Tachycardia Algorithm Utilized?
The PALS (Pediatric Advanced Life Support) Tachycardia Algorithm is a valuable tool that guides healthcare providers in managing rapid heart rates in pediatric patients. It provides a systematic approach to evaluating the condition of the child and administering appropriate treatments. By following this algorithm, healthcare providers can respond to pediatric tachycardia smoothly and provide prompt care for children in critical situations.
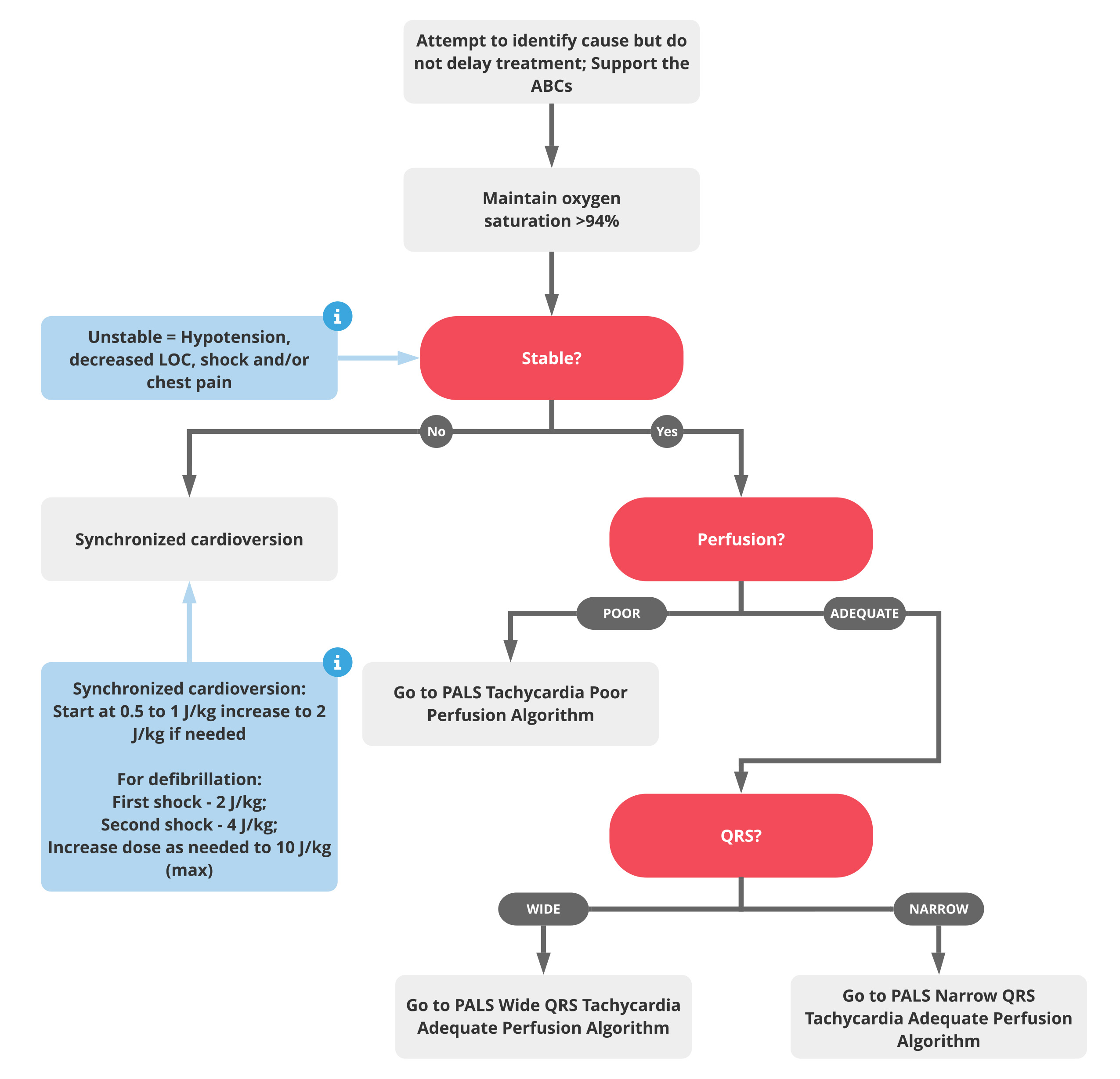
The algorithm outlines various interventions and serves as a step-by-step guide for healthcare providers. It starts with an initial assessment, evaluating the airway, breathing, and circulation, as well as assessing consciousness and signs of poor perfusion. Next, it involves determining the heart rate and rhythm through pulse palpation or ECG. The stability of the patient is then assessed based on clinical signs. For stable patients, the algorithm addresses reversible causes. For unstable patients, immediate interventions like synchronized cardioversion or medication administration are administered. Ongoing monitoring is crucial to assess the patient’s response and adjust the treatment accordingly. Collaborative care is also emphasized, promoting teamwork and communication among healthcare providers for coordinated care delivery.
What are the Key Components of the PALS Tachycardia Algorithm?
Understanding the components of the PALS (Pediatric Advanced Life Support) Tachycardia Algorithm is crucial for managing rapid heart rates in pediatric patients. This algorithm includes several unique components that are tailored to the specific needs of pediatric patients. It emphasizes the assessment and identification of reversible causes contributing to pediatric tachycardia, such as electrolyte imbalances or congenital heart defects. Age-appropriate medications are recommended to ensure safe and effective dosages and administration routes for pediatric patients. Considerations for pediatric cardioversion, including appropriate energy levels and sedation requirements, are outlined. Family involvement and support are also encouraged throughout the process to alleviate anxiety and allow room for understanding. The algorithm recognizes the unique physiological and anatomical differences in pediatric patients and requires tailored approaches to assessment and treatment. Effective communication among healthcare providers is stressed for coordinated and timely care delivery. Ongoing monitoring post-intervention is highlighted to assess treatment effectiveness and patient response. Continuous education and training are also encouraged to stay updated with evolving guidelines and practices in pediatric cardiac care.
What are the Different Pathways in the PALS Tachycardia Algorithm?
The PALS (Pediatric Advanced Life Support) Tachycardia Algorithm provides two structured pathways for managing rapid heart rates in pediatric patients. The first pathway is for stable tachycardia, which involves assessing and managing pediatric patients with a rapid heart rate who are hemodynamically stable. The second pathway is for unstable tachycardia, which focuses on immediate interventions for pediatric patients with a rapid heart rate who are hemodynamically unstable, aiming to restore perfusion.
How Does the PALS Tachycardia Algorithm Help in Pediatric Resuscitation?
The PALS Tachycardia Algorithm supports pediatric resuscitation efforts in several distinctive ways. It helps categorize patients into stable and unstable groups based on their hemodynamic status, allowing for targeted interventions. Immediate intervention guidelines ensure timely interventions such as synchronized cardioversion or medication administration to restore perfusion. The algorithm also provides recommendations for age-appropriate medication dosages and administration routes, improving medication efficacy and safety in pediatric patients. It outlines considerations for safe and effective cardioversion in pediatric patients, including appropriate energy levels and the need for sedation to minimize patient discomfort. Recognizing the importance of involving and supporting families throughout the resuscitation process, the algorithm fosters a collaborative approach and provides emotional support to caregivers. Effective communication among healthcare team members is emphasized, promoting clarity in decision-making during resuscitation. Ongoing patient monitoring allows for real-time assessment of treatment effectiveness and adaptation as needed.
Conclusion
The PALS Tachycardia Algorithm serves as a roadmap for healthcare professionals in addressing rapid heart rates in pediatric patients. By following this structured framework, medical teams can enhance coordination and make informed decisions, optimizing the care and survival rates of children facing cardiac challenges. The algorithm provides a systematic assessment and intervention process, leading to timely and precise treatment. It guides healthcare providers through all the major steps, ensuring that pediatric tachycardia is managed effectively and efficiently.

