Weaponized large language models (LLMs) are rapidly evolving and becoming increasingly challenging to stop. In response to this growing threat, Meta has developed CyberSecEval 3, a suite of security benchmarks designed to assess the cybersecurity risks and capabilities of AI models. This framework focuses on evaluating eight different risks across two categories: risk to third parties and risk to application developers and end users. The goal of CyberSecEval 3 is to get ahead of weaponized LLM threats and provide organizations with the tools to mitigate these risks effectively.
The comprehensive report published by Meta highlights critical vulnerabilities in their AI models, particularly Llama 3. This model has the capability to generate moderately persuasive multi-turn spear-phishing attacks, potentially scaling these threats to an unprecedented level. However, the report also emphasizes the need for significant human oversight in offensive operations involving Llama 3 to avoid critical errors. While Llama 3 can automate phishing campaigns, it still requires human intervention for complex cyber operations.
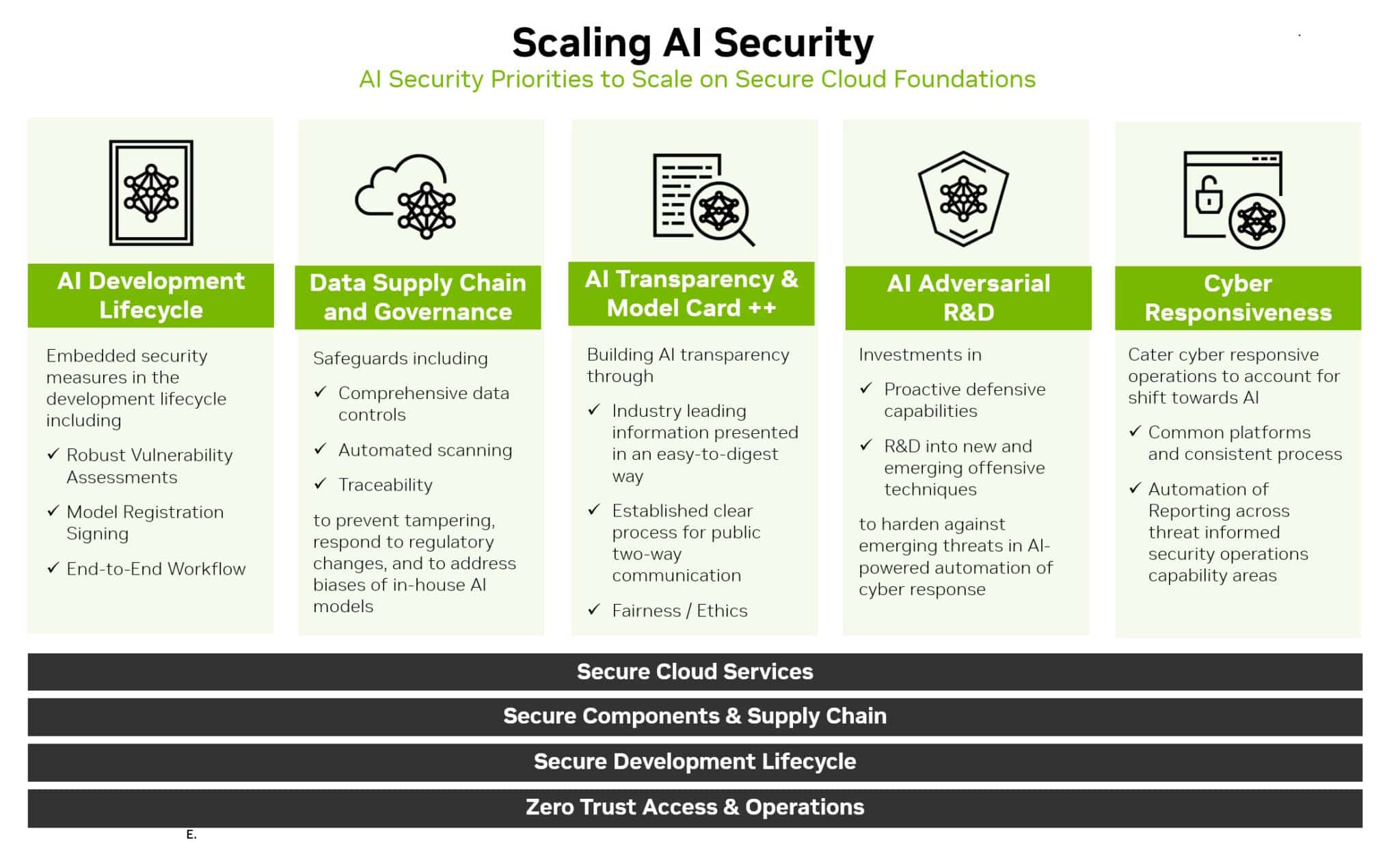
To combat weaponized LLMs effectively, organizations need to adopt several strategies outlined in the CyberSecEval 3 framework. These strategies include deploying advanced guardrails, enhancing human oversight in AI-cyber operations, strengthening phishing defenses, investing in continuous training, and adopting a multi-layered security approach. The data from the report supports each of these strategies, emphasizing the urgency of taking action before the threats become unmanageable.
Deploying tools like LlamaGuard 3 and PromptGuard can significantly reduce AI-induced risks by preventing models from being misused for malicious attacks. These tools have proven effective in reducing the generation of malicious code and the success rates of prompt injection attacks. Additionally, enhancing human oversight in AI-cyber operations is crucial, as LLMs still require close monitoring and guidance from human operators, particularly in high-stakes environments.
One of the critical risks identified in CyberSecEval 3 is the automation of spear-phishing campaigns by LLMs. To counter this threat, organizations should strengthen their phishing defense mechanisms through AI detection tools that can identify and neutralize phishing attempts generated by advanced models like Llama 3. Continuous investment in AI security training is also essential to keep cybersecurity teams updated on the latest AI-driven threats and equip them with the knowledge to effectively leverage LLMs for defensive purposes.
Finally, a well-defined, multi-layered security approach is vital in combating weaponized LLMs. Combining AI-driven insights with traditional security measures can significantly enhance an organization’s defense against various threats. Integrating static and dynamic code analysis tools with AI-driven insights can reduce the likelihood of deploying insecure code in production environments.
Meta’s CyberSecEval 3 framework provides a real-time, data-centric view of how LLMs become weaponized and offers actionable steps for organizations to mitigate the risks. By deploying advanced guardrails, enhancing human oversight, strengthening phishing defenses, investing in continuous training, and adopting a multi-layered security approach, enterprises can better protect themselves against AI-driven cyberattacks. Incorporating the CyberSecEval 3 framework into their broader cyber defense strategy for LLMs is essential for organizations already using or experiencing LLMs in production.

